Six Sigma - Defect Metrics
Before we go ahead, let us define two terms:
● A Six Sigma defect is defined as anything outside of customer specifications.
● A Six Sigma opportunity is the total quantity of chances for a defect.
This chapter provides a list formulae normally used to measure different metrics related to Six Sigma defects.
Defects Per Unit - DPU
Total Number of Defects
DPU = ------------------------
Total number of Product Units
DPU = ------------------------
Total number of Product Units
The probability of getting 'r' defects in a sample having a given DPU rate can be predicted with the Poisson Distribution.
Total Opportunities - TO
TO = Total number of Product Units x Opportunities
Defects Per Opportunity - DPO
Total Number of Defects
DPO = ------------------------
Total Opportunity
DPO = ------------------------
Total Opportunity
Defects Per Million Opportunities - DPMO
DPMO = DPO x 1,000,000
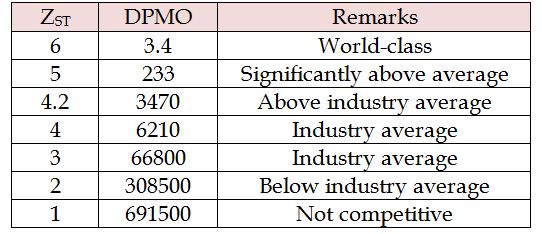
Defects Per Million Opportunities or DPMO can be then converted to sigma values using Yield to Sigma Conversion Table given in Six Sigma - Measure Phase.
According to the conversion table:
6 Sigma = 3.4 DPMO
How to find your Sigma Level
● Clearly define the customer's explicit requirements.
● Count the number of defects that occur.
● Determine the yield-percentage of items without defects.
● Use the conversion chart to determine DPMO and Sigma Level.
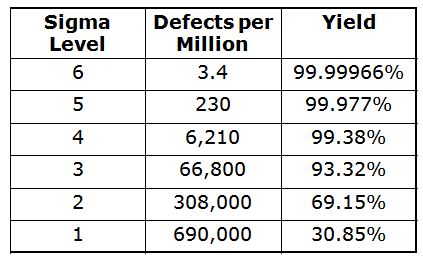
Simplified Sigma Conversion Table
If your yield is: Your DPMO is: Your Sigma is:
30.9% 690,000 1.0
62.9% 308,000 2.0
93.3 66,800 3.0
99.4 6,210 4.0
99.98 320 5.0
99.9997 3.4 6.0
30.9% 690,000 1.0
62.9% 308,000 2.0
93.3 66,800 3.0
99.4 6,210 4.0
99.98 320 5.0
99.9997 3.4 6.0
Six Sigma - Summary
We can summarize the following points:
● Six Sigma is a philosophy of quality improvement.
● Six Sigma is 3.4 defects in one million opportunities (DPMO).
● Components of Six Sigma are Customer, Process, and Employees.
● Six Sigma implementation requires the following roles:
○ Business Leader
○ Sponsor
○ Black Belt
○ Master Black Belt
○ Green Belt
● The generic cycle of Six Sigma includes the following phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control.
● Six Sigma is dedicated to 'Customer focus'.

Comments
Post a Comment